Overview
This guide walks you through setting up a secure connection from xpander to AWS Redshift Serverless using IAM credentials and Secrets Manager authentication. This approach provides a secure, scalable way to query your Redshift data warehouse without exposing database credentials directly.
By the end of this tutorial you will have an AI agent capable of query data from redshift
Architecture
The connection uses a layered security approach:
IAM User: Provides AWS-level permissions to access Secrets Manager and Redshift Data API
Secrets Manager: Securely stores the actual Redshift database credentials
Redshift Data API: Executes queries using credentials from Secrets Manager
This means your IAM user acts as a secure intermediary - it can retrieve credentials and execute queries, but the actual database permissions are controlled by the Redshift user stored in the secret.
Prerequisites
Before you begin, ensure you have:
AWS account with permissions to create IAM users and policies
Redshift Serverless workgroup or provisioned cluster
Database credentials stored in AWS Secrets Manager
xpander account with connector configuration access
Step 1: Create IAM User with Required Permissions
Create the IAM User
Create Secrets Manager Policy
This policy allows the IAM user to read your Redshift credentials:
Save this as redshift-secret-policy.json and create the policy:
Create Redshift Data API Policy
This policy allows the IAM user to execute queries via the Redshift Data API:
Create the policy
Attach Policies to User
Create Access Keys
Save the output - you'll need the AccessKeyId and SecretAccessKey for Xpander configuration.
Step 2: Store Redshift Credentials in Secrets Manager
If you haven't already stored your Redshift database credentials in Secrets Manager:
Note the Secret ARN from the output - you'll need it for xpander connector screen.
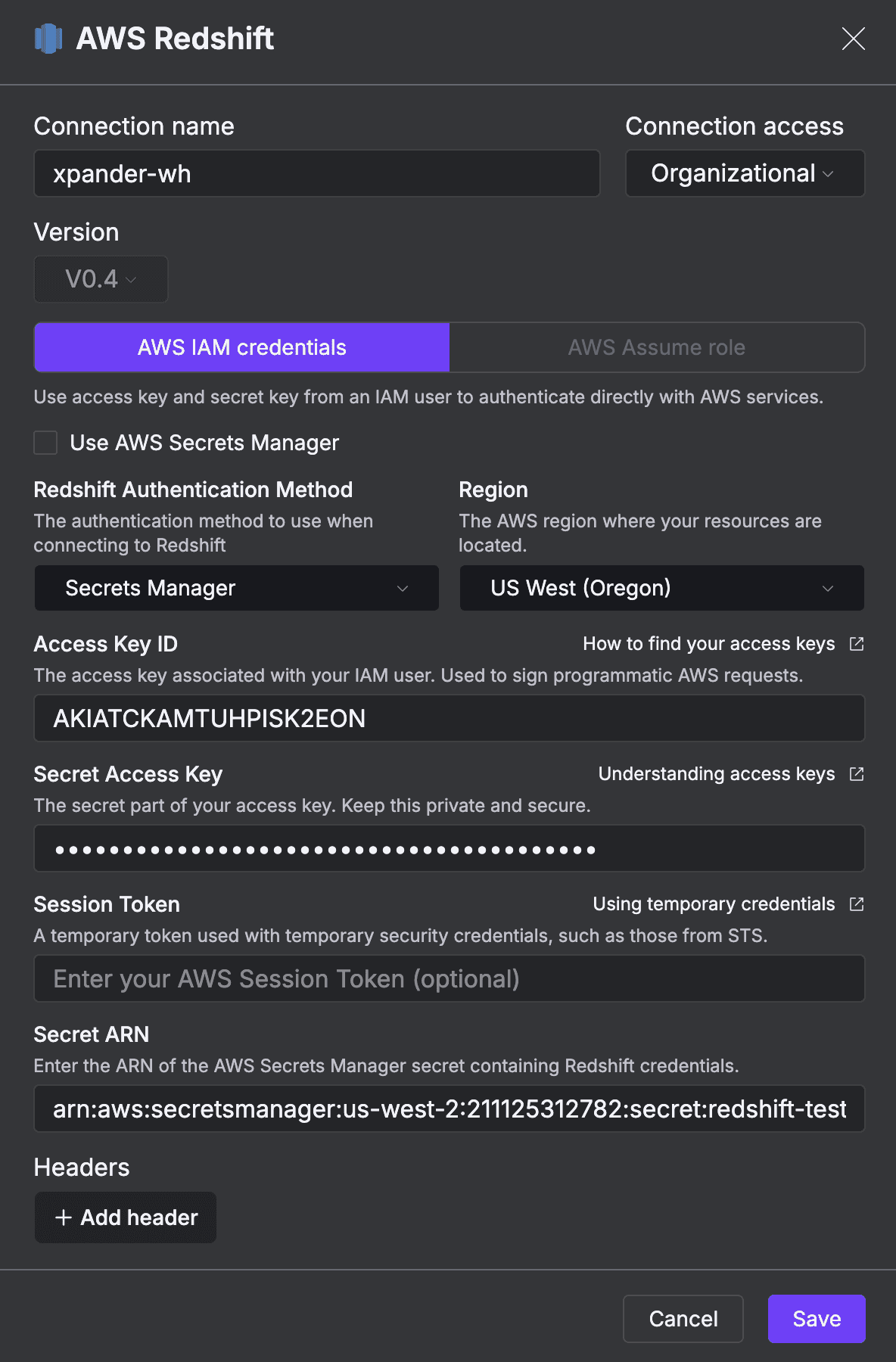
Step 3: Configure xpander Redshift Connector
Now that your AWS infrastructure is ready, configure the connector in xpander:
Navigate to Connectors : Go to Settings → Connectors. Click Add Connector. Select AWS Redshift
Fill in the following fields:
Service: AWS Redshift
Connection Name: xpander-wh (or your preferred name)Authentication Settings
Method Type: AWS IAM credentials
Redshift Authentication Method: Secrets Manager
Region: US West (Oregon) / us-west-2
IAM Credentials
Access Key ID: <your-access-key> (from Step 1.5)
Secret Access Key: <your-secret-key> (from Step 1.5)
Session Token: Leave empty (not needed for standard IAM users)
Secrets Manager Configuration
Secret ARN: this-is-the-arn-secret-of-the-user-with-data-access
Example: